39 字符串类的创建(上)
字符串类的创建
-
历史遗留问题
- C语言不支持真正意义上的字符串
- C语言用字符数组和一组函数实现字符串操作
- C语言不支持自定义类型,因此无法获得字符串类型
-
从C到C++的进化过程引入了自定义类型
-
在C++中可以通过类完成字符串类型的定义
问题:C++中的原生类型系统是否包含字符串类型?
-
KylinLib中字符串类的设计 -
KylinLib中字符串类的实现class String : public Object
{
public:
String();
String(const char *s);
String(const String &s);
int length() const;
const char* str() const;
/*比较操作符重载函数*/
/*加法操作符重载函数*/
/*赋值操作符重载函数*/
~String();
protected:
void init(const char *s);
char *m_str;
int m_length;
} -
实现时的注意事项
- 无缝实现String对象与char*字符串的互操作
- 操作符重载函数需要考虑是否支持
const版本 - 通过C语言中的字符串函数实现String的成员函数
编程实验
-
字符串类的实现
//KylinString.h
#ifndef KYLINSTRING_H
#define KYLINSTRING_H
#include "Object.h"
namespace KylinLib {
class String
{
public:
String();
String(const char c);
String(const char *str);
String(const String &str);
String& operator=(const String &str);
String& operator=(const char *str);
const char* str()const;
size_t length() const;
bool operator< (const char *str);
bool operator< (const String &str);
bool operator>= (const char *str);
bool operator>= (const String &str);
bool operator> (const char *str);
bool operator> (const String &str);
bool operator<= (const char *str);
bool operator<= (const String &str);
bool operator== (const char *str);
bool operator== (const String &str);
bool operator!= (const char *str);
bool operator!= (const String &str);
String& operator+= (const char *str);
String& operator+= (const String &str);
String operator+(const char *str);
String operator+(const String &str);
protected:
void init(const char *str);
private:
char *m_str = nullptr;
size_t m_length = 0;
};
}
#endif // KYLINSTRING_H//KylinString.cpp
#include "KylinString.h"
#include "Exception.h"
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
namespace KylinLib {
String::String()
{
init("");
}
String::String(const char c)
{
char str[]={c,'0'};
init(str);
}
String::String(const char *str)
{
init(str);
}
String::String(const String &str)
{
init(str.m_str);
}
String &String::operator=(const String &str)
{
return operator=(str.m_str);
}
String &String::operator=(const char *str)
{
if(m_str!=str){
auto s = strdup(str);
if(s==nullptr)
THROW_EXCEPTION(NoEnoughMemoryException,"Thers is no memory to aclloc string...");
free(m_str);
m_str = s;
m_length = strlen(m_str);
}
return *this;
}
const char *String::str() const
{
return m_str;
}
size_t String::length() const
{
return m_length;
}
bool String::operator<(const char *str)
{
return (strcmp(m_str,str)<0);
}
bool String::operator<(const String &str)
{
return operator<(str.m_str);
}
bool String::operator>=(const char *str)
{
return !(*this<str);
}
bool String::operator>=(const String &str)
{
return !(*this<str);
}
bool String::operator>(const char *str)
{
return (strcmp(m_str,str)>0);
}
bool String::operator>(const String &str)
{
return operator>(str.m_str);
}
bool String::operator<=(const char *str)
{
return !(*this>str);
}
bool String::operator<=(const String &str)
{
return !(*this>str);;
}
bool String::operator==(const char *str)
{
return (strcmp(m_str,str)==0);
}
bool String::operator==(const String &str)
{
return operator==(str.m_str);
}
bool String::operator!=(const char *str)
{
return !(*this==str);
}
bool String::operator!=(const String &str)
{
return !(*this==str);
}
String &String::operator+=(const char *str)
{
if(str!=nullptr){
auto s = reinterpret_cast<char*>(malloc(m_length+strlen(str)));
if(s==nullptr)
THROW_EXCEPTION(NoEnoughMemoryException,"Thers is no memory to alloc string...");
strcpy(s,m_str);
strcat(s,str);
free(m_str);
m_str = s;
m_length = strlen(m_str);
}
return *this;
}
String &String::operator+=(const String &str)
{
return operator+=(str.m_str);
}
String String::operator+(const char *str)
{
String ret;
ret+= *this;
ret+= str;
return ret;
}
String String::operator+(const String &str)
{
return operator+(str.m_str);
}
void String::init(const char *str)
{
m_str = strdup(str?str:"");
if(m_str==nullptr)
THROW_EXCEPTION(NoEnoughMemoryException,"Thers is no memory to aclloc string...");
m_length = strlen(m_str);
}
}
小结
- C/C++语言本身不支持字符串类型
- C语言通过字符数组和一组函数支持字符串操作
- C++通过自定义字符串类型支持字符串操作
- 字符串类型通过C语言中的字符串函数实现
40 字符串类的创建(下)
字符串类的创建
-
字符串类中的常用成员函数
成员函数 功能描述 operator[ ](i) 操作符重载函数,访问指定下标的字符 startWith(s) 判断字符串是否以s开头 endOf(s) 判断字符串是否以s结束 insert(i,s) 在字符串的位置i处插入s trim() 去掉字符串两端的空白 -
重载数组操作访问符[ ]
char& operator\[ ](int i);char operator\[](int i)const;
-
注意事项
- 当i的取值不合法时,抛出异常
- 合法范围:
(0<=i)&&(i<m_length)
-
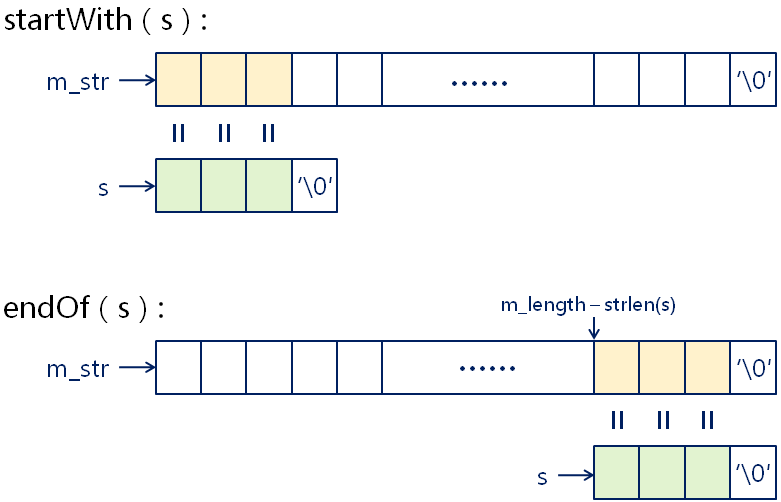
判断是否以指定字符串开始或结束
bool startWith(const char *s)const;bool startWith(const String &s)const;bool endOf(const char *s)const;bool endOf(const String &s)const;
-
在指定位置插入字符串
String& insert(int i,const char* s);String& insert(int i,const String &s);
-
去掉字符串两端的空白字符
String& trim();
编程实验
-
常规成员函数的实现
思考:
如何在目标字符串中查找是否存在指定的子串?
String s = 'Hello World!";
int pos = s.indexOf("o"); //4